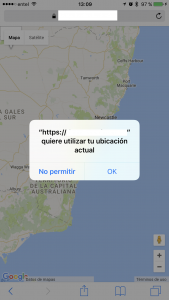
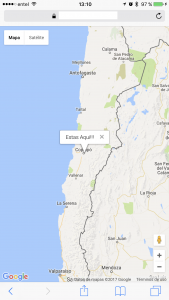
El título lo dice casi todo. La idea es mostrar la ubicación de la persona que abre un sitio web sobre el mapa de Google.
Hay que considerar lo siguiente:
– La dirección web debe ser https.
– La geolocalización puede ser apróximada dependiendo de la fuente utilizada (Dirección IP o GPS).
– El usuario debe autorizar a la aplicación (o sitio web) para que pueda utilizar la geolocalización.
Debes tener en cuenta que para este ejemplo debes activar una API KEY de Google Maps Javascript API.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Geolocation</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="initial-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no">
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
#map {
height: 100%;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map"></div>
<script>
function initMap() {
var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), {
center: {lat: -34.397, lng: 150.644},
zoom: 6
});
var infoWindow = new google.maps.InfoWindow({map: map});
// HTML5 geolocation.
if (navigator.geolocation) {
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(position) {
var pos = {
lat: position.coords.latitude,
lng: position.coords.longitude
};
infoWindow.setPosition(pos);
infoWindow.setContent('Estas Aqui!!!');
map.setCenter(pos);
}, function() {
handleLocationError(true, infoWindow, map.getCenter());
});
} else {
// Si el navegador no soporta Geolocation
handleLocationError(false, infoWindow, map.getCenter());
}
}
function handleLocationError(browserHasGeolocation, infoWindow, pos) {
infoWindow.setPosition(pos);
infoWindow.setContent(browserHasGeolocation ?
'Error: Servicio de Geolocation fallo.' :
'Error: Tu navegador no soporta geolocation.');
}
</script>
<script async defer
src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?key=TU_API_KEY&callback=initMap">
</script>
</body>
</html>
Y este sería el resultado:
- Ejemplo extraido de la Documentacion Google Maps API